Small Molecule Active Peptide
precision craftsmanship of nutrition
What is Small Molecule Active Peptide?
Definition: Small-molecule active peptides refer to short chains of amino acids, typically containing fewer than 50 amino acid residues, with bioactive properties. These peptides exhibit functional activities at the cellular or molecular level, influencing various biological processes.
Production and Engineering:
Synthetic Biology:
- Engineered through advanced synthetic biology techniques for precise control over sequence and function.
- Allows customization of peptides for specific applications.
Biotechnological Processes:
- Manufactured through biotechnological methods, often involving microbial fermentation or recombinant DNA technology.
- Production processes aim for high purity and yield.
Applications:
Pharmaceuticals:
- Utilized in drug development for targeted therapeutic effects.
- Examples include peptides designed to mimic natural regulatory molecules.
Cosmetics:
- Integrated into skincare products for anti-aging or skin-renewal effects.
- Peptides may stimulate collagen production or influence skin cell behavior.
Product Center
Classification of Small-Molecule Active Peptides
Structural Classification:
- Linear Peptides: These have a straightforward, unbranched sequence.
- Cyclic Peptides: Form a closed loop structure, often enhancing stability and bioactivity.
Function-Based Classification:
- Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Combat against microorganisms, showcasing potential applications in medicine and agriculture.
- Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs): Facilitate the delivery of molecules into cells, holding promise in drug delivery.
Source-Based Classification:
- Animal-Derived Peptides: Extracted from animals, such as marine organisms, insects, or mammals.
- Plant-Derived Peptides: Sourced from plants and often associated with various biological activities.
Activity Classification:
- Enzyme Inhibitors: Peptides that inhibit specific enzymes, often with applications in drug development.
- Neuroactive Peptides: Influencing neurological processes and functions.
Chemical Structure Classification:
- Dipeptides, Tripeptides, Oligopeptides: Based on the number of amino acid residues.
- Modified Peptides: Includes peptides with chemical modifications to enhance stability or bioavailability.
Target-Specific Classification:
- Receptor-Binding Peptides: Interact with specific receptors, often used in drug design.
- Ion Channel-Modulating Peptides: Influence ion channel activity, holding potential in neurology and cardiology.
Understanding these classifications provides insights into the diverse nature of small-molecule active peptides and their potential applications in various fields.
Application of Small-Molecule Active Peptides

What Do You Need?
Solutions For Every Need
GUGU’s products are built upon a foundation of precise engineering, diverse applications, and a commitment to sustainability and eco-friendliness. You deserve solutions that are as versatile as your needs. We’ve created a line that is right for you, no matter where you are or what you are facing.



Typical Small-molecule Peptide Manufacturing Process
The first step involves designing the desired peptide sequence based on the intended application.
Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) is a common method used for peptide assembly. It involves building the peptide chain step by step on a solid support.
Amino acids are coupled together in a series of chemical reactions to form the peptide chain.
The coupling reactions involve activating the carboxyl group of one amino acid and then reacting it with the amino group of another amino acid.
After each coupling step, protective groups are removed to expose reactive sites for the next coupling reaction.
This process continues until the full peptide sequence is assembled.
Once the peptide chain is complete, it is cleaved from the solid support, leaving the peptide in a crude form.
The crude peptide undergoes purification processes to remove any impurities and by-products.
Techniques such as chromatography are commonly used for purification.
The purified peptide is analyzed to confirm its identity, purity, and sequence.
Mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are commonly used for analysis.
The final purified peptide is often lyophilized to create a stable, dry powder form.
This process involves freezing the peptide and then removing the ice through sublimation.
Stringent quality control measures are implemented to ensure the final product meets specified standards.
This may include testing for potency, purity, and absence of contaminants.
It’s important to note that the production of peptides can vary depending on factors such as the specific synthesis method, the complexity of the peptide sequence, and the intended application of the final product. Additionally, adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP) is crucial, especially in the production of peptides for pharmaceutical and clinical applications.
Spray Drying or Freeze-drying
In the peptide manufacturing process, the drying form can vary, and commonly used methods include spray drying or freeze-drying (lyophilization). Both methods serve to remove the liquid component and stabilize the peptide for storage. The choice between spray drying and freeze-drying depends on various factors, including the characteristics of the peptide and the desired properties of the final product.
Spray Drying
- Process: In spray drying, a liquid peptide solution is atomized into fine droplets and introduced into a hot air chamber. The droplets quickly evaporate, leaving behind dried particles.
- Advantages: It is a relatively fast process, suitable for large-scale production. It can be more cost-effective for certain peptides.
Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization)
- Process: Freeze-drying involves freezing the peptide solution and then removing the ice by sublimation under vacuum conditions. This results in a dry, porous structure.
- Advantages: It is a gentle process that helps preserve the peptide’s structural integrity. It is often preferred for heat-sensitive peptides.
The choice between spray drying and freeze-drying depends on factors such as the stability of the peptide, the desired characteristics of the final product, and the scale of production. Both methods aim to produce a stable, dry form of the peptide that can be easily stored and reconstituted when needed.
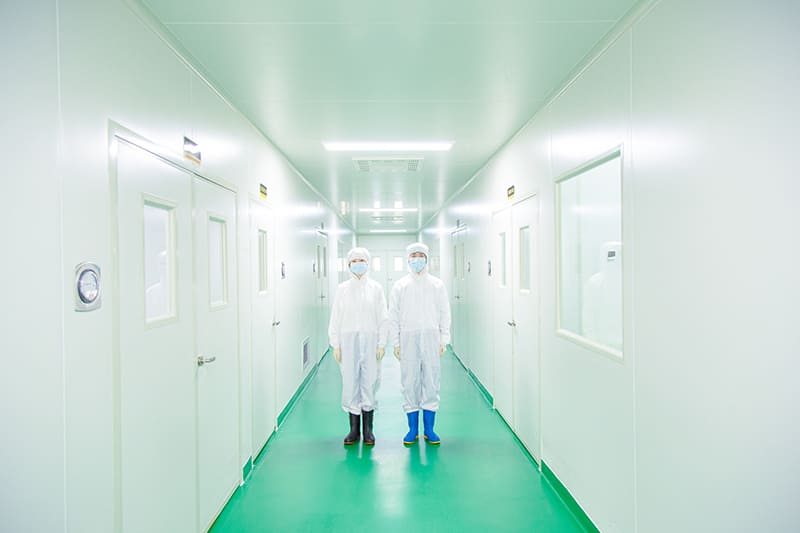
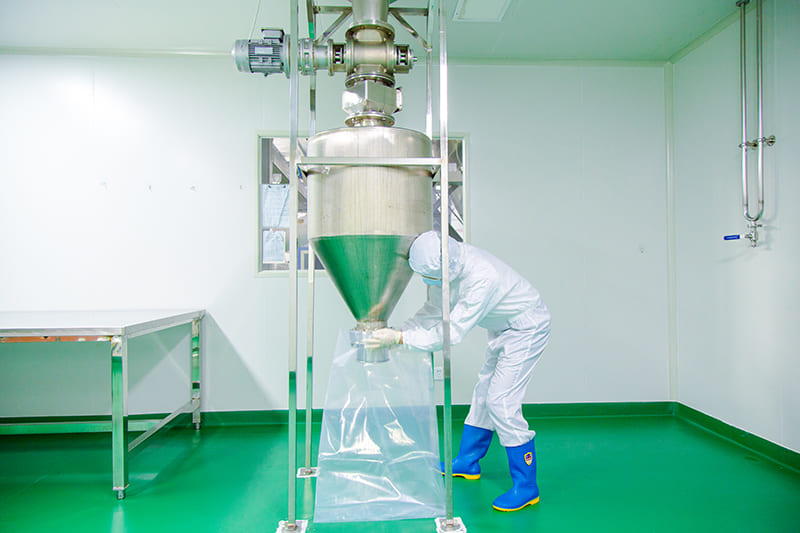
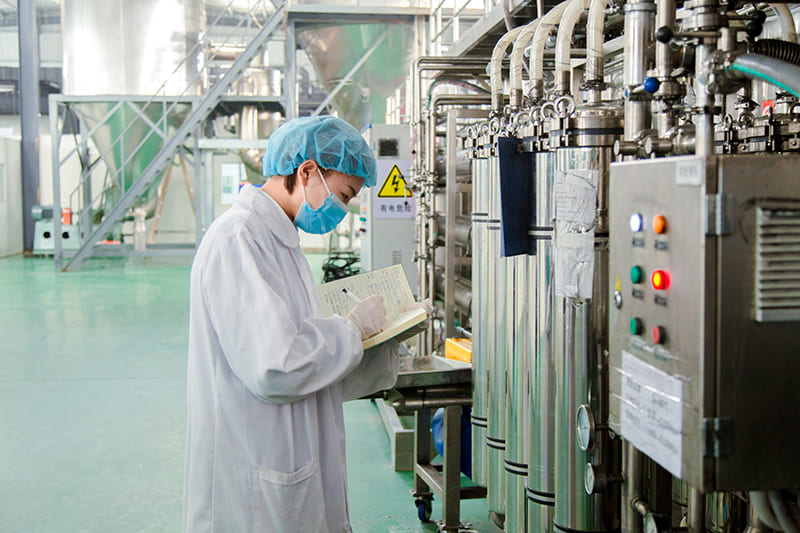
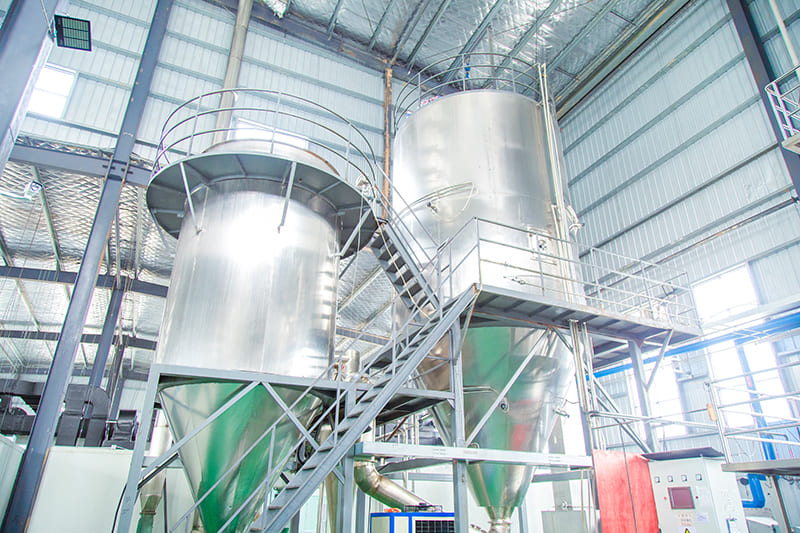
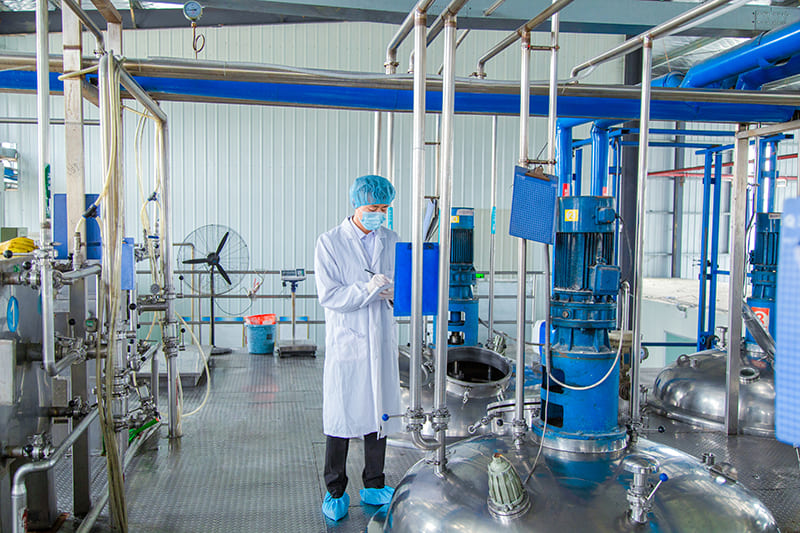
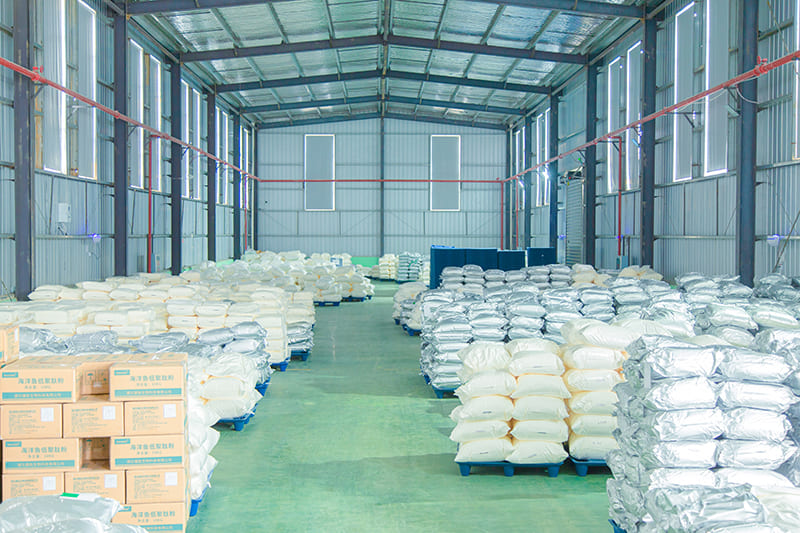









Our Quality
The factory core advantage is that we have mastered the world’s leading biological enzymatic hydrolysis technology, membrane separation and low-temperature concentration production process, obtained a number of industrial technical patents .We can customize products according to the requirements of client from different industries. Packaging workshop is established in accordance with GMP standards and we already passed certificate ISO 22000 / FDA/ HALAL / HACCP etc. At present, can produce various collagen products, such as animal origin collagen like fish collagen, bovine collagen, type II collagen peptide, marine fish oligopeptide; plant origin collagen like pea protein, soybean protein, corn oligopeptide etc. They are widely used in food ingredient, health care, cosmetics, pharmacy filed.

We Have Great Answer
Frequently Asked Questions
If your question is not listed, please email us right now.
The distinction lies in size. Small molecule peptides typically consist of fewer amino acids, offering unique advantages in terms of applications and bioavailability compared to larger counterparts.
In cosmetics, these peptides often contribute to anti-aging formulations, promoting skin elasticity, and aiding in the reduction of fine lines and wrinkles.
Yes, many small molecule peptides align with eco-friendly practices. Their applications in biodegradable materials and sustainable processes contribute to environmentally conscious solutions.
Absolutely. They find applications in agrochemicals, enhancing plant growth, and providing protection against pests. This contributes to sustainable agricultural practices.
Yes, they play a crucial role in medicine. From drug development to diagnostic tools, small molecule peptides showcase versatility in addressing various health-related challenges.
These peptides often exhibit excellent biological compatibility, making them suitable for various applications in the medical and cosmetic fields without adverse reactions.
Their small size allows for efficient drug delivery, penetrating cellular membranes with ease, and enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of medications.
Their inherent stability often enhances the shelf life and efficacy of formulations, ensuring a consistent and reliable product over time.
Indeed, their compatibility allows for synergistic effects, amplifying the overall performance and benefits when combined with complementary components.
Yes, our innovative processes allow for the customization of peptides, tailoring them to meet the specific requirements of diverse industries.
Absolutely, we offer resources and support to enhance understanding, ensuring our clients are well-informed about the potential and applications of small molecule peptides.
We are committed to sustainable practices, including eco-friendly sourcing of raw materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Our products strictly adhere to GMP standards, ensuring quality and safety in every step of the manufacturing process.
Our small molecule peptides are rigorously tested and certified, meeting international standards for quality and safety.
Rigorous quality control measures are in place, guaranteeing consistency in the performance and properties of our small molecule peptides
We strive to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring the highest quality, offering value for your investment.
Our team is well-versed in regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance with international standards and addressing regulatory challenges proactively.
Yes, our research team is actively involved in continuous exploration, aiming to uncover new applications and advancements in the field of small molecule peptides.
The the current trends and innovations in the field of small-molecule active peptides
**1. Personalized Medicine:
- Tailoring small-molecule active peptides for individualized therapeutic interventions.
- Precision medicine approaches that consider genetic and molecular profiles for targeted treatments.
**2. Bioinformatics and Computational Design:
- Integration of bioinformatics and computational tools for designing novel peptides.
- Predictive modeling to optimize peptide structures for specific functions or interactions.
**3. Peptide Therapeutics for Cancer:
- Advancements in using peptides for targeted cancer therapies.
- Peptide-based drug delivery systems designed for enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects.
**4. Immunomodulatory Peptides:
- Exploration of peptides with immunomodulatory properties for treating autoimmune diseases.
- Designing peptides to modulate immune responses for therapeutic applications.
**5. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs):
- Continued research on AMPs as alternatives to traditional antibiotics.
- Development of AMPs with enhanced stability and efficacy against multidrug-resistant pathogens.
**6. Innovations in Drug Delivery:
- Peptide-based delivery systems with improved bioavailability and targeted release.
- Nanoparticle formulations for transporting peptides to specific tissues or cells.
**7. Cross-Industry Collaborations:
- Increasing collaborations between the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and agricultural sectors.
- Shared expertise leading to innovative applications of small-molecule active peptides across industries.
**8. Synthetic Biology and Directed Evolution:
- Using synthetic biology techniques to engineer peptides with desired properties.
- Directed evolution approaches for optimizing peptide sequences for specific functions.
**9. Neuroactive Peptides for Brain Disorders:
- Research on neuroactive peptides for potential applications in treating neurological disorders.
- Peptide-based interventions designed to modulate neural activity for therapeutic purposes.
**10. Sustainable Agriculture: – Application of small-molecule active peptides in sustainable agriculture practices. – Peptide-based solutions for enhancing plant growth, nutrient uptake, and stress resistance.
These trends highlight the dynamic and evolving nature of small-molecule active peptides, showcasing their potential in addressing diverse challenges and creating innovative solutions across various fields.
By following these guidelines, you can make informed decisions when selecting food additives, ensuring that they not only meet the functional requirements but also align with quality, safety, and consumer preferences
Characteristics of small-molecule active peptides
Size:
- Small-molecule active peptides are characterized by their relatively small size compared to larger proteins. Their compact structure is composed of a limited number of amino acid building blocks.
Bioactivity:
- These peptides possess specific biological activities, interacting with various biomolecules or cellular components. Their bioactivity can range from enzymatic inhibition to receptor binding.
Functionality:
- Small-molecule active peptides often serve specific functions within biological systems. They can act as signaling molecules, regulators of cellular processes, or even as therapeutic agents.
Versatility:
- These peptides demonstrate versatility in their applications. They find utility across different industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and biotechnology, showcasing their adaptability.
Structural Diversity:
- The structural diversity of small-molecule active peptides includes linear sequences, cyclic forms, and modified structures. These variations contribute to their stability, bioavailability, and specific functions.
Cellular Penetration:
- Some small-molecule active peptides, known as cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), have the ability to facilitate the entry of molecules into cells. This property is valuable in drug delivery applications.
Source Variation:
- Small-molecule active peptides can be derived from different sources, including animals, plants, or synthesized through laboratory methods. The source can influence their properties and applications.
Target Specificity:
- Many small-molecule active peptides exhibit target specificity, interacting with specific receptors, enzymes, or cellular structures. This specificity is crucial in their therapeutic or regulatory roles.
Biological Significance:
- Despite their small size, these peptides often play significant roles in biological systems, contributing to essential functions, regulatory pathways, and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Understanding these characteristics provides insight into the diverse and impactful nature of small-molecule active peptides, making them valuable components in various scientific, industrial, and medical applications.
