Table of Contents
Habitat
Edelweiss is adapted to high-altitude environments, typically found at elevations between 1,800 to 3,400 meters above sea level in the European mountain ranges such as the Alps, Pyrenees Mountains, and the Italian Apennines.These conditions include low atmospheric pressure, higher ultraviolet radiation, and extremes in temperature and humidity.The plant prefers rocky limestone places, which contributes to its unique living situation and survival strategies.
Not only life in the high altitudes, but also its sophisticated blooming process make the Edelweiss such an extremely rare and precious Alpine plant. Edelweiss does not bloom in the first year of culture and it can only be harvested from the 2nd to the 4th year of its life.

How is Leontopodium alpinum extract produced and what parts of the plant are used?
Leontopodium alpinum extract, commonly derived from the Edelweiss plant, is produced using various parts of the plant, including the aerial parts and roots. The production process typically involves the use of solvents to extract the active compounds from the plant material.
Production Process
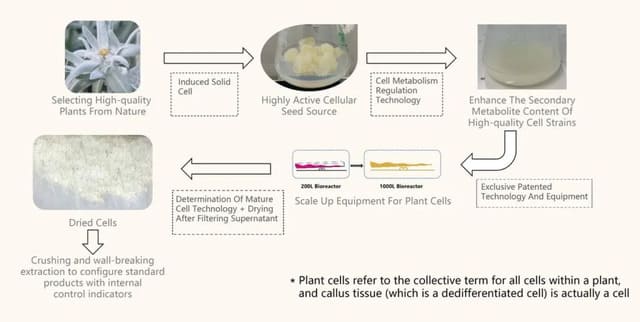
The extract can be obtained through different extraction methods, such as using dichloromethane, methanol, or CO2 to extract compounds from the aerial parts and roots of the plant.Additionally, callus culture extracts can be produced from the leaves of the plant. Callus culture involves inducing undifferentiated plant cells to form a callus, which can then be used to produce extracts in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and concentration of active compounds.
LEONTOPODIUM ALPINUM CALLUS CULTURE EXTRACT
Used Plant Parts
The sub-aerial parts of the plant, which are above ground, such as the leaves and flowers, are commonly used for extraction. The roots of the plant are also used, particularly for their rich content of active compounds that may have medicinal properties. The specific variety of Leontopodium alpinum known as ‘Helvetia’ is cultivated at high altitudes in the Alps and is used for its high levels of active compounds like leontopodic acid and flavonoids.
Active components in Leontopodium alpinum extract

Leontopodium alpinum contains several active components that contribute to its medicinal and cosmetic properties.
Chlorogenic Acid: This compound exhibits antioxidant activity, which can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants are crucial in skincare as they can slow down the aging process and improve skin health
Leontopodic Acids: These are phenylpropanoids that are considered the main active substances in Edelweiss extracts. Leontopodic acid A, in particular, has been found to effectively boost COI-1 expression, hinder MMP-1 expression, and curb ROS and Ca2+ endocytosis, which are processes related to inflammation and cellular damage.
Isoquercitrin, Isochlorogenic Acid A, Cynaroside, Syringin, Isochlorogenic Acid, Cynarin, Rutin, and Leontopodic Acid B: These compounds were identified in a study investigating the blue light-damage-protecting activities of Leontopodium alpinum callus culture extract. They were found to have protective effects against blue light-induced cell injury.
Luteolin-4′-O-glucoside, Apigenin-7-glucoside, Luteolin, Tannin, and β-Sitosterol: These compounds are also found in Edelweiss extract and contribute to its beneficial properties.
How is Leontopodium alpinum extract used in skincare and cosmetic products?

Leontopodium alpinum extract, derived from the Edelweiss plant, is incorporated into skincare and cosmetic products primarily for its antioxidant and skin-soothing benefits. The extract contains constituents that help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals and environmental aggressors, such as certain types of airborne pollutants.This makes it particularly valuable in anti-aging formulations, as it can slow down the aging process and improve skin health.
In cosmetic products, Leontopodium alpinum extract is used in a variety of product types, including anti-aging creams, around-eye creams, facial cleansers, moisturizers, serums, and sun care products. Its high Radical Protection Factor (RPF) indicates a strong ability to combat free radicals, which is twice as potent as vitamin C.
This potent antioxidant activity not only protects the skin but also helps to repair already damaged or prematurely aged skin, reducing fine lines and wrinkles.



Furthermore, the extract is known for its lifting action, as demonstrated in in-vivo tests where it tightened sagging skin on the neck and smoothed out crow’s feet wrinkles.It also delivers beneficial hydration, increases skin plumpness, and builds resilience against dryness.In summary, Leontopodium alpinum extract is used in skincare and cosmetic products for its antioxidant, skin-soothing, anti-aging, and hydrating properties, making it a valuable ingredient for maintaining and improving skin health and appearance.
Recommended dosage or concentration of Leontopodium alpinum extract in skincare products
The recommended dosage or concentration of Leontopodium alpinum extract in skincare products varies depending on the specific application and formulation.
For skincare products, a concentration of 3-5% is often recommended. This is based on a product description from a natural organic skincare company, which suggests adding 27 drops for a 3% concentration and 45 drops for a 5% concentration in a one-ounce formula.
In the context of cosmetic applications, a brochure from a producer of organic extracts suggests a concentration of 1-3% for their Leontopodium alpinum extract product, which is intended for use in anti-aging/sagging skin care products and day care protecting formulations.
However, it’s important to note that the optimal concentration may depend on the specific formulation of the product, the desired effects, and the individual’s skin type and sensitivity. Therefore, manufacturers and consumers should follow the guidelines provided by the extract supplier or consult with a skincare professional for personalized advice.
Production and Sustainability
Due to its rarity and the environmental impact of harvesting it from the wild, there are indeed sustainability concerns associated with the production of Leontopodium alpinum extract.
However, several measures have been taken to address these concerns. For instance, some companies have developed unique high-altitude cultivation processes to produce Edelweiss extracts.
In addition, biotechnological methods have been employed to produce Leontopodium alpinum extract. One such method involves the use of plant callus cultures, which are unorganized or undifferentiated cell masses that can be artificially cultured by adding nutrients and plant growth regulators in antiseptic conditions.This method allows for the production of a high number of specific plant cells with equal quality in a bioreactor, thereby reducing the need for wild harvesting.
Another biotech process, known as HTN™ technology, is used to produce Leontopodium alpinum extract in a way that preserves the rare and strictly protected plant.This process is described as totally eco-sustainable。
Despite these efforts, it’s important to note that the demand for Leontopodium alpinum extract could potentially lead to overharvesting and low natural availability of the plant.Therefore, ongoing efforts to ensure sustainable harvesting and production practices are crucia.








